Double-clicking an icon is easy, but it leaves you in the dark when things go wrong. If you are trying to debug a crashing program, pass specific startup arguments, or just want to feel like a power user, the Command Prompt (CMD) is your best friend. Running an executable from the command line gives you full control over the process, allowing you to catch error messages that usually disappear in a fraction of a second.
Whether you are a developer testing a build or a gamer trying to launch a server with custom flags, mastering these commands is essential.
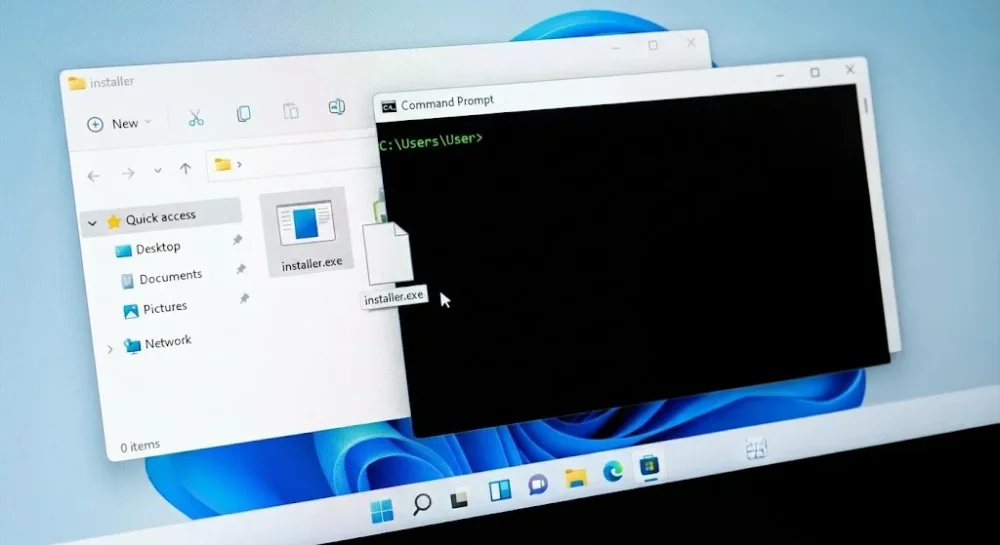
The Drag & Drop Method (Easiest Way)
If you are not comfortable typing long file paths or worried about making a typo, this trick is a lifesaver. You don't need to memorize the exact location of your file.
- Open Command Prompt (Press
Win + R, typecmd, and hit Enter). - Type the name of the program you want to run (if it's in the system path) or just leave the cursor blinking.
- Open the folder containing your
.exefile in File Explorer. - Drag the file and drop it directly into the black CMD window.
Windows will automatically paste the full path for you, complete with quotation marks if there are spaces in the folder names. Press Enter, and you are good to go.
The Professional Method: Using cd Command
While drag-and-drop is great for one-off tasks, you will often need to work within a specific directory, especially if your program relies on other files (like .dll or config files) in the same folder. This is where the cd (Change Directory) command comes in.
Navigating to Folders
To switch to the folder where your application lives, use the cd command followed by the path.
cd C:\Users\YourName\DownloadsOnce you are in the correct directory, you can simply type the name of the file (e.g., program.exe) to run it. If you are looking to manage system behaviors or restart services after this, knowing how to reboot windows cmd can also be very useful for your workflow.
Handling Spaces in Paths
This is the most common error beginners face. If your folder name has a space, like Program Files, CMD might misinterpret it as two separate commands. To fix this, always wrap your path in double quotes.
cd "C:\Program Files\My Application"Switching Drives (The /d Trick)
By default, the cd command acts within the current drive (usually C:). If your game or program is installed on a secondary drive like D: or E:, typing cd D:\Games won't work on its own. You need to add the /d switch.
cd /d D:\Games\MyGameHow to Run EXE with Administrator Privileges
Some programs require elevated permissions to modify system files or write to protected folders. If you try to run them from a standard CMD window, you might get an "Access Denied" error.
To solve this, you don't need a special code inside the terminal. Instead, you must launch the terminal itself with high privileges:
- Press the Windows key and type
cmd. - Right-click on Command Prompt.
- Select Run as administrator.
Now, any .exe you launch from this window will inherit those admin rights. This is often necessary when setting up system-level tools or modifying environment variables for your development setup.
Advanced: Passing Arguments & Logging Output
Command-line tools often accept "arguments" (or flags) that change their behavior. These are specific instructions written after the file name.
For example, to run a program in "silent" mode or force a specific resolution, you might type:
setup.exe /silent /norestartSaving the Output (Logging)
If a program runs too fast and you can't read the text it spits out, you can redirect that output to a text file using the > symbol. This is incredibly useful for troubleshooting.
diagnose.exe > log.txtAfter running this, nothing will appear on the screen, but a file named log.txt will be created in that folder containing all the output.
Troubleshooting: Why Does My Program Close Instantly?
You double-click an EXE, a black window pops up, and then it vanishes instantly. This happens because the program finishes its task (or crashes) and Windows closes the session immediately.
To see what happened, do not double-click. Instead:
- Open CMD first.
- Navigate to the folder using the
cdcommand. - Run the executable by typing its name.
By doing this, the CMD window stays open even after the program terminates, allowing you to read any error messages or exit codes. If you are moving towards more complex scripting, you might also want to explore PowerShell scripts as a more modern alternative to batch files and CMD commands.




Comments (0)
Sign in to comment
Report